Many homeowners encounter common problems with toilet water supply lines, such as leaks and corrosion. Timely intervention is crucial. As mentioned earlier, early detection saves time and money:
| Scenario | Detection Cost | Repair Cost | Total Cost | Additional Costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Detection | $300 | $200 | $500 | Minor Impact |
| Delayed Detection | $400 | $10,300 | $10,700 | Weeks of disruption, potential health issues |
High-quality braided hoses help prevent leaks and rust in toilet water supply lines. People should look for signs of problems such as leaks or loose parts to prevent larger issues.
Key Takeaways
- Check your toilet water supply line regularly to detect leaks early. Look for water stains or dirt on the floor.
- Use high-quality materials, such as braided stainless steel hoses. These hoses are less prone to rust and leaks. They have a longer lifespan and help keep your home safe.
- Make sure all connections are tightened. Replace any hoses that look damaged immediately. Performing these simple maintenance tasks can prevent you from incurring hefty repair costs later.
- Understand what clogs the toilet, such as excess toilet paper or wipes. Don’t flush down items that can’t be broken down in water. This helps keep the water flowing smoothly.
- Know when you need to replace your water supply pipes. Most water supply pipes have a lifespan of about ten years. Replace them if you find rust or damage.
Common Problems with Toilet Water Supply Line
Causes of Water Supply Line Leak
Many common toilet water supply pipe problems begin with leaks. Plumbers often identify several reasons for leaking toilet water supply pipes. A worn-out stop valve can cause water to seep into the toilet. A failed wax ring can cause water to pool around the bottom of the toilet bowl. A loose or damaged water supply pipe can cause visible puddles near the toilet. Cracks in the tank or toilet seat can also cause leaks. An overfilled float ball or float cup can cause water to overflow into the overflow pipe. Corrosion of the flush valve seals, exposed to minerals in the water, can damage them and cause leaks. Every valve in the system plays a role in preventing these problems. Regularly checking the water supply valves helps detect problems early.
Signs of Leaking Toilet Supply Line
Common toilet problems can be identified by observing common signs of a leaking toilet supply pipe. Water accumulation around the toilet seat is a sign of malfunction. Soft spots or discoloration on the bathroom floor usually indicate a leak. Peeling grout near the fixtures may mean water is leaking from the supply pipe. An unpleasant odor or recurring musty smell near the toilet indicates a hidden leak. Water stains, peeling paint, or bulging drywall on the ceiling or walls indicate water has leaked outside the bathroom. Unexplained water bill spikes and a persistent running sound also indicate a toilet leak. A gurgling sound from the drain pipe may mean there is a leak in the supply pipe. Checking the water supply valve and the leaking area at the toilet seat helps pinpoint the problem.
Fixing a Water Supply Line Leak
Toilet repairs begin with finding the source of the leak. Before starting any repairs, turn off the water supply valve. Tighten any loose connections on valves and water supply pipes. Replace damaged hoses or broken joints. Using high-quality materials can prevent common toilet problems in the future. If the leak is caused by a faulty wax ring or stop valve, replace these parts. If the leak is in the toilet base, remove the toilet and install a new wax ring. Clean and dry the leaking area before reinstalling the toilet. After repairs, test the water supply valve and check for leaks. Anyone wanting to know how to repair a leaking toilet water supply pipe should follow these steps. Regular maintenance and timely repairs will ensure your toilet water supply pipes function properly.
Toilet Supply Line Corrosion and Rust Issues
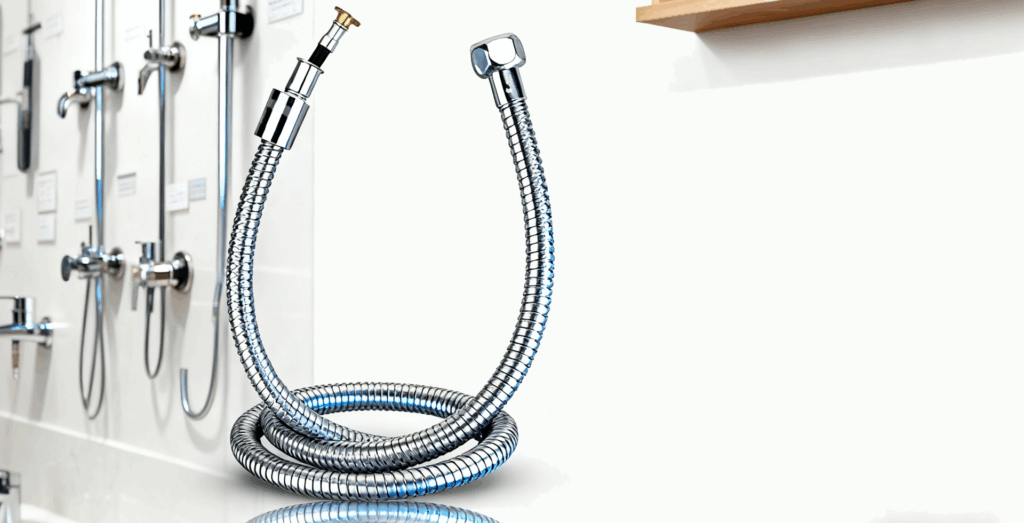

Why Toilet Supply Line Corrosion Happens
Corrosion is usually caused by the pipe material. Metal pipes such as copper, galvanized steel, and cast iron will rust over time. Hard water rich in minerals accelerates corrosion. Acidic water with a low pH can also damage metal pipes. Sometimes, contact between different metals can also cause problems. Stray currents and oxygen in the water can also weaken the pipes. Hot water and dirt inside the pipes can also cause damage. Using strong drain cleaners or improper pipe installation can create weak points in the pipes.
- Materials prone to rust:
- Copper (better than steel, but still rusts)
- Galvanized steel (rusts very easily)
- Cast iron (cast iron pipes commonly found in older houses rust easily)
- Materials that do not rust:
- PVC
- CPVC
- PEX
Spotting Corrosion
Homeowners can look for signs of rust in their pipes. Rust spots or unusual discoloration on pipes indicate corrosion. Peeling or bubbling in pipes are also warning signs. Water stains on the floor or walls near the toilet may indicate a problem. Low water pressure or leaks may mean the pipes are rusting inside. Professionals use specialized tools to inspect pipes for rust. These tools include X-rays, magnetic field detectors, and resistance probes. They can detect rust without disassembling the pipes.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Insulation Removal | Removing the insulation to inspect the pipes; this method is best suited for stainless steel pipes. |
| Infrared Detection | Detecting damp spots in the insulation may indicate rust. |
| Radiographic Testing | Using X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the inside of the pipes for problems. |
| Magnetic Flux Leakage | Using a magnet to detect rust; suitable for routine inspections. |
| Electrical Resistance Probes | Determining the presence of rust by detecting changes in resistance. |
Solutions for Corrosion
The first step in solving rust problems is to locate the problem. If you find leaks or low water pressure, plan for repairs or replacement of the pipes. Choosing the right materials is crucial. Experts recommend using rust-resistant PEX pipes or braided hoses. When repairing pipes, workers must prepare the site properly and install new parts correctly. After repairs, conduct a leak test to ensure effectiveness. Record the repair details for future reference. Regularly inspecting pipes and using high-quality materials can prevent rust from recurring.
Tip: Using newer braided hoses, such as those from the GONGGONG brand, helps prevent rust and extends the life of your toilet’s water supply lines.
Toilet Supply Line Loose or Faulty Connections
Common Toilet Problems with Connections
Toilets often experience problems due to faulty or worn connections. Plumbers report several common malfunctions that can lead to leaks or other issues with the water supply lines. These include:
- Loose or worn water supply pipes
- Worn gasket between the tank and toilet seat
- Loose toilet base bolts
- Cracked tank
- Failed wax ring seal
Any of these issues can cause leaks or an unstable toilet. Water supply valves and other valves must be kept tight to prevent leaks. Regular inspections help detect and resolve problems before they escalate.
Symptoms of Loose Connections
Loose toilet connections can cause many warning signs. Homeowners should look for the following:
- Visible puddles near the toilet
- Dripping water or dampness on the pipes
- Muddy or musty smell
- Water stains on the floor or walls
- Increased water bills
Water supply leaks usually start as small leaks but can quickly escalate. If you feel the water supply valve or other valves are loose, this may indicate a problem. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should check all valves and connections.
Tip: Early detection of leaks can save money and avoid larger repair costs.
How to Tighten or Replace Connections
Repairing loose connections or replacing faulty water supply pipes can ensure your toilet functions properly. You can perform the repair by following these steps:
- Turn the water supply valve clockwise to turn off the water supply.
- Flush the tank to empty it and dry any remaining water with a towel.
- Use a wrench to loosen the water supply pipe nuts at the water supply valve and toilet inlet valve.
- Remove the old water supply pipe and inspect all valves and connections for damage.
- Tighten the nuts at both ends by hand to install the new water supply pipe.
- Turn the water supply valve counterclockwise to restore water flow.
- Check all connections for leaks and tighten as needed.
Good maintenance requires the use of high-quality parts and ensuring all valves and connections are secure. Regularly checking the water supply valve and other valves helps prevent future problems. If the water supply pipe leaks again, the entire pipe may need to be replaced.
Damaged or Cracked Toilet Supply Line
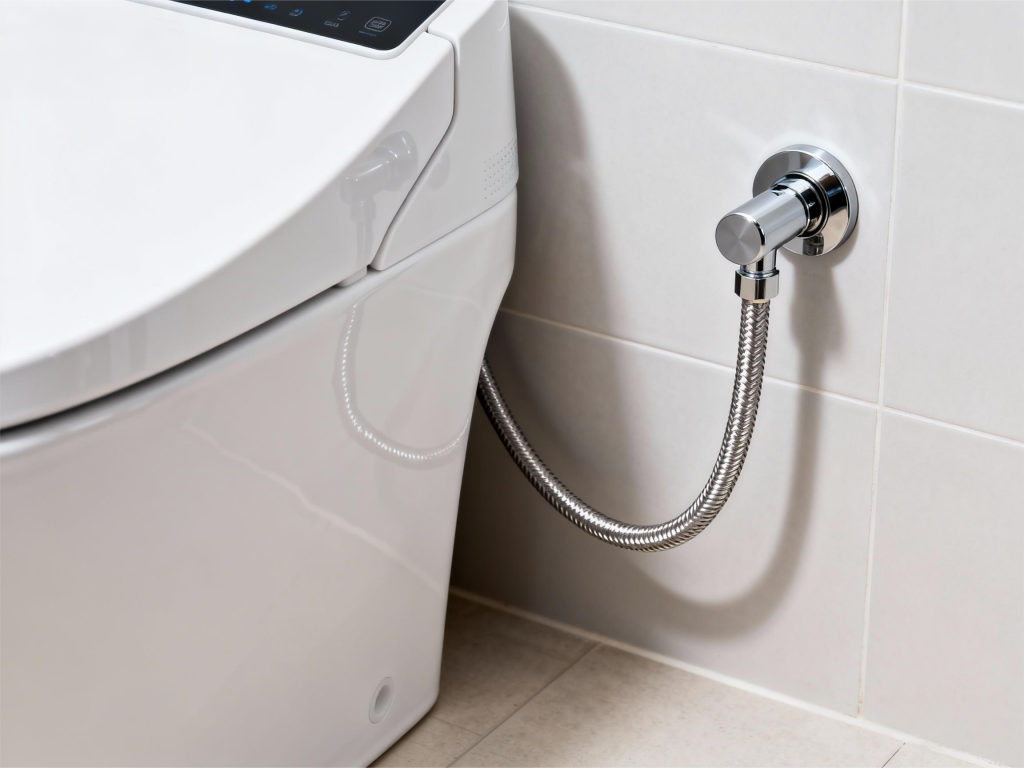

Causes of Hose Damage
Toilet water supply hoses can fail for a variety of reasons. Over time, hoses age due to use. Excessive water pressure can put too much stress on the hose. Extremely hot or cold temperatures can cause the hose to crack. Sometimes, plumbers apply pipe sealant to the plastic threads. They may also overtighten the plastic nuts. This can cause the nuts to break and leak. A rubber hose with a braided stainless steel outer layer can last about ten years. Without proper maintenance, the hose will fail much faster. A damaged water supply valve can also damage the hose. Minerals in the water can cause the hose to rust. Improper installation can also lead to premature failure.
- Common causes of hose failure:
- Wearing out of old hoses
- Cracks caused by excessively cold or hot weather
- Damaged water supply valve
- Improper installation
- Excessive water pressure
- Rust caused by minerals in the water
- Neglecting hose maintenance
Warning Signs of Damage
A toilet with a broken or cracked hose will show obvious signs of damage. Water may accumulate around the toilet seat. The hose may appear swollen or have visible cracks. Sometimes, water drips from the hose or its connection. If the leak goes undetected, mold can grow. If water pressure drops rapidly, the hose may be the problem. If the toilet is constantly running or the floor feels soft, check the hose. A damaged gasket or seal can also cause leaks at the hose end.
Tip: Regularly check the hose and connections for signs of dampness or damage.
Steps to Replace Damaged Hoses
Replacing a damaged toilet hose ensures your bathroom stays safe and dry. First, turn off the water supply. Flush to empty the tank. Loosen the nuts at both ends of the hose with a wrench. Remove the old hose and check both ends for damage. Install the new braided hose and tighten the nuts by hand. Turn the water supply back on and check for leaks. Flush the toilet a few times to test. If no leaks are found, the replacement is complete. Regularly checking the hose helps prevent future problems.
Toilet Supply Line Blockages and Reduced Flow
Causes of Blockages
There are many reasons why toilet water pipes can become clogged. People often flush down items that are difficult to decompose. These items can accumulate and obstruct water flow. Some of the most common causes include:
- Excessive toilet paper
- Baby wipes and “flushable” wipes
- Paper towels and napkins
- Feminine hygiene products
- Dental floss
- Cotton swabs and pads
- Hair
- Oil
When these items get into the water supply line, they can cause leaks or slow water flow. Debris buildup inside the valves can also cause blockages. Regularly checking the valves helps prevent these problems.
Identifying Flow Problems
Reduced toilet water flow usually has some noticeable signs. The tank may fill more slowly after flushing. The toilet may not flush completely. Sometimes, leaks in the water supply line can occur near valves or hoses. People may hear a gurgling sound or notice a weak flush. If the valve feels tight or difficult to turn, it may be internally blocked. Water stains around valves or hoses can also be a sign of malfunction. Checking valves and hoses for buildup helps detect problems early.
Tip: If the toilet takes longer to fill than usual, check valves and hoses for blockages.
Fixing Blockages
Most clogs can be cleared with simple tools and steps. First, shut off the water flow by turning off the valve. Use a plunger to unclog the drain. If the plunger doesn’t work, try using a drain auger. Insert the drain auger into the drain and turn the handle to clear the blockage. For minor clogs, pour hot water or a mixture of baking soda and vinegar into the toilet. Dish soap can also help loosen the blockage. If the blockage is near the valve, disconnect the hose and clean the valve opening. After clearing the blockage, be sure to check the water supply for leaks. Reopen the valve and observe for any leaks or slow water flow. Regular cleaning and careful use help keep valves and water supply lines clear.
Preventing Common Toilet Supply Line Problems
Regular Inspection Tips
Homeowners can prevent many toilet water supply problems through regular inspections. Check the toilet monthly to detect leaks or loose valves early. Every three months, carefully check the area around valves or hoses for mold or rust. Have a plumber inspect your entire water supply system annually, especially if your home is old or if there’s a leak before the toilet. Look for musty smells, unusually high water bills, or unusual noises from the pipes. These signs may indicate a problem with the toilet’s water supply lines or valves. If you encounter any serious issues, contact a plumber to ensure a lasting, effective, and safe repair.
When to Replace Toilet Water Supply Line
Knowing when to replace old pipes helps prevent leaks. Most water supply lines have a lifespan of about ten years, but some types last much longer. The table below shows the lifespan of different pipe materials:
| Pipe Material | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Copper | 50–70+ years |
| Galvanized Steel | 20–50 years |
| Brass | 40–70 years |
| Cast Iron | 75–100 years |
| PVC | 25–40 years |
| CPVC | 50–75 years |
| PEX | 40–50 years |
| Lead | 100+ years |
If you find wear, leaks, or rust on your toilet water supply pipes, repair or replace them promptly. Regularly inspect the water supply valve and hose connections to detect and address problems before they worsen. Replacing old pipes before they burst can save on repair costs.
Choosing Quality Materials
Choosing the right material for your toilet water supply pipes is crucial. For example, braided stainless steel hoses, such as GONGGONG braided stainless steel hoses, are sturdy, durable, and less prone to tangling or rusting. These hoses help protect valves and water supply pipes for a long time. Flexible hoses are easy to install and help prevent leaks. While they are more expensive than plastic hoses, they last longer and provide better protection for your home. Plastic nuts may break after a few years, leading to leaks and water damage. Polyoxymethylene (POM) plastic may crack under stress, causing valve failure. Using sturdy hoses and metal fittings helps prevent leaks and reduces the frequency of repairs.
Tip: High-quality water supply pipes and regular inspections contribute to the long-term stable operation of your toilet and water supply valves.
Toilet water supply pipes often experience problems such as leaks, rust, or blockages. Ignoring these issues can damage your home, leading to poor water quality and costly repairs. Regularly checking your toilet helps detect leaks early. For safety, it’s recommended to use a sturdy and durable hose like GONGGONG braided hoses. If your toilet continues to leak or flushes poorly, you may need to seek professional help. Serious problems should be handled by a reputable and insured plumber to ensure the safety of your home.
FAQ
What is the best material for toilet water supply lines?
Stainless steel braided hoses are the best choice for toilet water supply lines. They are rust-resistant and durable. Brands like GONGGONG offer robust, durable, and flexible products. These hoses help prevent leaks and pipe damage.
How often should toilet water supply lines be checked?
It is recommended to check toilet water supply lines every few months for leaks, rust, or loose connections. Early checks help prevent major problems. For added safety, a plumber may check the lines annually.
Can homeowners replace toilet water supply lines themselves?
Yes, homeowners can replace the toilet water supply hose themselves. The replacement process only requires simple tools such as a wrench. Clear instructions will help simplify the process. If problems arise, a plumber can be called for assistance.
What causes a toilet water supply hose to burst?
Excessive water pressure, aging hoses, or poor-quality materials can all cause bursts. Low temperatures can also damage hoses. Regularly inspecting and using high-quality hoses, such as GONGGONG braided hoses, can reduce the risk of bursting.
How long does a braided toilet water supply hose last?
Braided hoses typically last 10 years or more. High-quality hoses may last even longer. If leaks, rust, or cracks appear, replace the hose. Regular inspections help ensure bathroom safety.